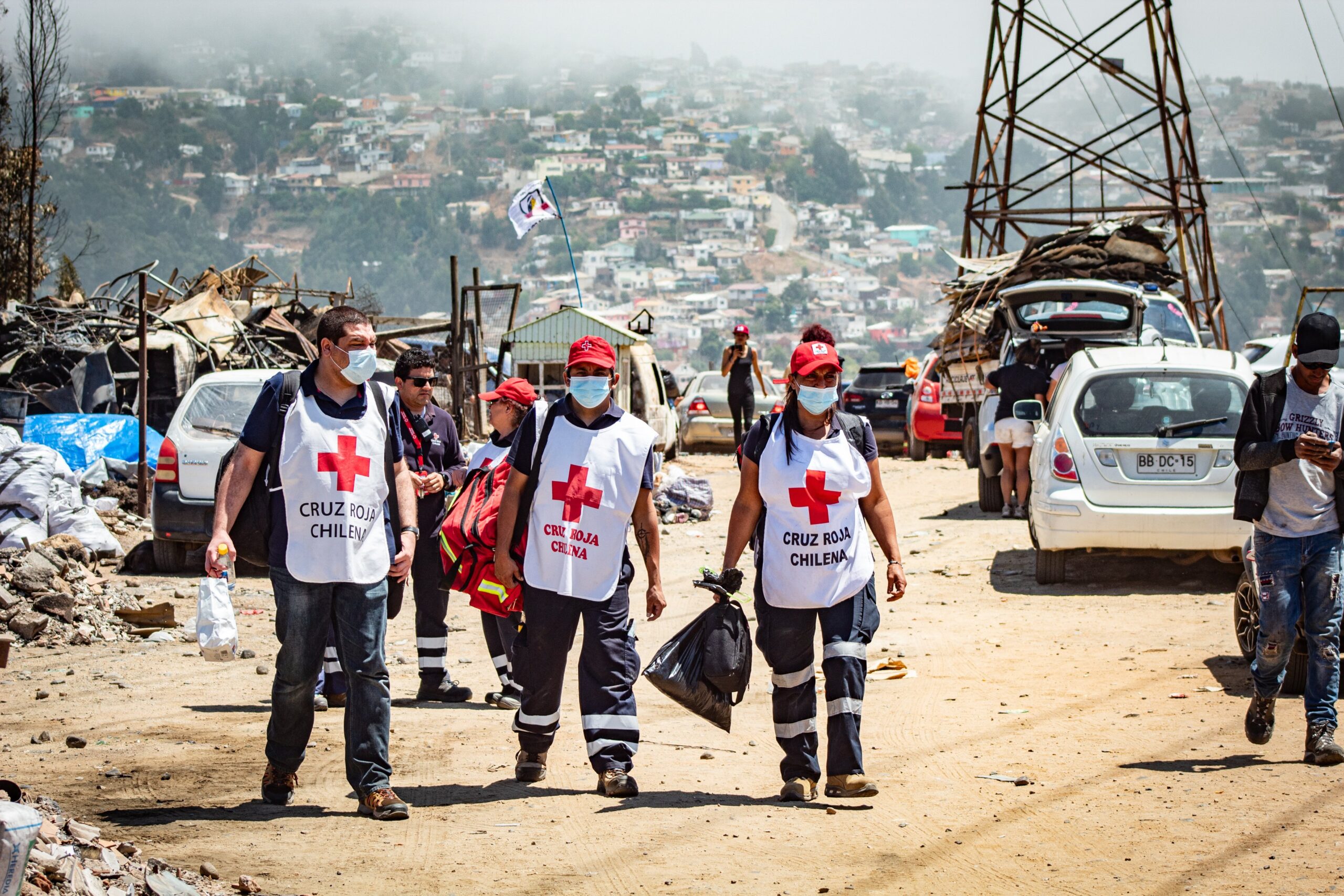
Excessive wildfires in coastal-central Chile have been fuelled by intense and chronic fire-conducive climate situations within the area for the reason that starting of the yr favouring the unfold of extreme fires in Viña del Mar (33°S, 71°W) in early February.
Through the early days of February 2024, a low-pressure system fashioned alongside the coast of central Chile, a widely known phenomenon affecting the western coast of subtropical South America, often known as the coastal low.
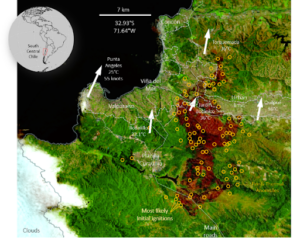
It results in clear skies and excessive temperatures in addition to sturdy winds as a result of an inverted strain gradient between an intense subtropical excessive extending properly into midlatitudes and the coastal low farther north. These situations are extremely conducive to wildfires i.e favour unfold, particularly throughout summer time when situations are hotter and drier. On February 2, 2024, wildfires ignited within the mountainous forested areas east of, forested areas east of town Viña del Mar and round Lake Peñuelas.
The flames quickly superior into densely populated metropolis outskirts regardless of authorities’ efforts to curb their unfold. The humanitarian impression continues to worsen, with over 29,000 hectares burnt since February 4, leading to 132 deaths, 300 lacking, 7,200 homes destroyed and 40,000 individuals affected.
Researchers from Chile, Brazil, Colombia, the Netherlands, Germany, Sweden and the UK collaborated to evaluate to what extent human-induced local weather change altered the chance and depth of the climate situations on the time of the fires, and the way the situations will likely be affected with additional warming.
Hearth climate is outlined by a mixture of elevated temperatures, diminished humidity, minimal rainfall, and heightened winds persisting over a interval. To seize the traits of this occasion, we use a hearth climate index (HDWI) primarily based on excessive wind speeds, excessive temperatures and low humidity. Whereas not taking the build-up of gas into consideration like different, extra advanced indices, it’s an efficient hazard metric for estimating risk to communities and problem of containment. We focussed on a coastal area affected by the wildfires that embrace Valparaíso and Viña del Mar.
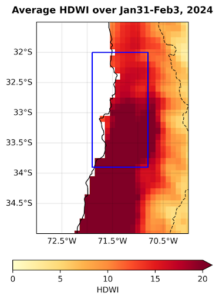
Determine 2 reveals the index values for the 4 days of highest hearth depth, when most impacts occurred.
Essential findings
- There may be important interplay between excessive local weather situations and land administration insurance policies, resulting in significantly devastating impacts in casual settlements.
- Hearth climate is one necessary issue that drives wildfires, though modifications in vegetation (wildfire gas), ignition elements, and hearth administration methods additionally contribute to future wildfire danger (‘danger’ refers back to the mixture of hazard, publicity and vulnerability, following widespread utilization in local weather science).
- To mix the completely different variables resulting in excessive hearth hazard we compute the new dry windy index (HDWI) that mixes excessive temperatures, excessive wind speeds and low humidity. On this index, we discover that the new, dry and windy situations that drove the wildfires of February 2024 are characterised as a 1 in 30-year occasion in at the moment’s local weather.
- To evaluate the position of local weather change, we mix observation-based merchandise and local weather fashions and assess modifications within the chance and depth of a 1-in-30-year 4-day occasion over the area of essentially the most devastating fires (fig. 2).
- We discover that total, there’s a small improve within the HDWI within the observations and a few fashions, however it’s not important. That is additionally true for the person elements of the index: most temperature, relative humidity and wind velocity, none of which present a major pattern.
- These outcomes should not shocking, given the coastal location of the area which has a properly established wind-driven sea floor temperature cooling.
- The fires occurred within the coastal vary of central Chile, proper within the transition of coastal cooling and inland warming, rendering it tough for many local weather fashions to signify the occasion properly. Solely 5 fashions have been in a position to simulate the occasion, and solely 2 of those carry out properly within the mannequin analysis, thus outcomes are very unsure. Moreover, the observation-based information are additionally comparably quick and extremely unsure, significantly with respect to the wind part.
- Nonetheless, until the world quickly stops burning fossil fuels, hearth hazard as a result of excessive HDWI will improve. Utilizing the identical restricted fashions as above, in a world 2°C hotter than preindustrial, the pattern in the direction of greater HDWI turns into important.
- We conclude that regardless of the pattern in HDWI not but being important, the danger of a rise in harmful hearth climate situations attributable to human-induced local weather change must be taken very significantly.
- We then assess to what extent El Niño is said to harmful hearth climate situations. We check two completely different indices to characterise the affect of El Niño and discover that El Niño has no important affect on the HDWI.
- Throughout the studied space, hearth danger is rising notably as a result of present land administration practices, such because the growth of Wildland-City Interface areas (together with the expansion of casual settlements in forest zones) and widespread conversion from native to international and monoculture plantations.
- The prevailing investments in hearth prevention and adaptation measures, coupled with low-risk notion amongst residents in fire-prone areas, have proven restricted effectiveness in adequately mitigating the hearth danger.
- Spared by the lethal flames, the pilot fireproofing program of Villa Botania
showcases the life-saving potential of preparedness, together with measures akin to community-led vegetation management, embedding water factors throughout the land, and sturdy emergency coaching. - Measures to deal with the numerous hearth danger ought to embody improved spatial planning; enhanced coordination, useful resource allocation, and group engagement in hearth prevention and adaptation; and consciousness elevating campaigns








