Below the affect of a lingering anticyclone, Fennoscandia skilled extraordinarily chilly winter temperatures throughout early January 2024.
In early January, very chilly air plenty from the Arctic flowed from the northeast over Northern Fennoscandia, with clear-sky secure situations permitting the floor to chill additional nonetheless over a big space. Very low temperatures had been measured at a number of stations/places, together with Enontekiö airport in Finland (-44.3°C on 5 January). On January 6, the chilly air mass shifted in the direction of Southern Scandinavia, with a document low reached in Bjørnholt, Oslo (-31.1 °C).
Whereas Fennoscandia is properly accustomed to and ready for winter situations, very low temperatures have turn into much less frequent within the latest a long time and occasions corresponding to this have the ability to shock and be notably impactful. Direct impacts of the coldwave may have been felt most strongly by susceptible teams notably individuals experiencing power poverty, residing in poor housing inventory, and/or experiencing homelessness. Aged individuals and youngsters are additionally extra susceptible physiologically to excessive temperatures. The chilly additionally triggered visitors disruptions, college closures, energy cuts and infrastructure harm.
Scientists from Norway, Sweden, Finland, France, the Netherlands, the UK and the US collaborated to evaluate whether or not and to what extent human-induced local weather change has modified the probability and depth of this chilly wave.
Revealed peer-reviewed strategies had been utilized by the group to analyse the occasion, on twodifferent scales and places: Firstly the annual (Jul-Jun) minimal of 5-day averaged minimal temperatures in a area impacted by the onset of the chilly wave in Northern Scandinavia, as proven in Determine 1; and secondly the single-day (Jul-Jun) minimal temperature for the station of Oslo, to the south of the research area, impacted barely later.
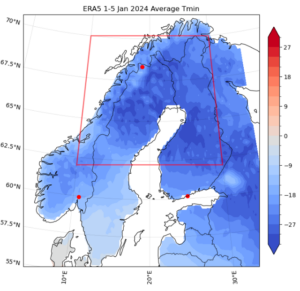
Primary findings
● Excessive chilly corresponding to skilled throughout this occasion can have extreme direct impacts on well being, and secondary impacts on roads, electrical energy grids, and providers corresponding to colleges and public transport.
● Chilly waves, like different excessive climate occasions, put vital strain on power, healthcare, and water programs. These programs should be designed and in a position to soak up extra (or completely different) wants, and early warnings, preparedness plans, and response capability are all essential to mitigate the impacts of those occasions.
● Homelessness particularly, but additionally power poverty and bottlenecks with the related value hikes and, in some circumstances, poor housing situations, exacerbate the impacts of chilly waves on notably susceptible socio-economic and demographic teams.
● Despite the fact that some very low temperatures had been recorded, the dataset based mostly on observations characterises the realm common 5-day chilly spell as a 1-in-15 12 months occasion in at the moment’s local weather, rating as twelfth coldest since 1950. For Oslo, the at some point minimal temperature was uncommon, roughly a 1-in-200 12 months occasion in at the moment’s local weather.
● To estimate the affect of human-caused local weather change on this excessive chilly we use a mixture of local weather fashions and the observations. We discover that due to human-induced local weather change the area-averaged occasion would have been about 4 levels colder in a 1.2°C cooler local weather. This corresponds to such chilly spells having turn into about 5 occasions much less frequent.
● For the Oslo station the chilly single day minimal would even have been about 4 levels colder with out human-induced local weather change. This corresponds to such chilly days having turn into about 12 occasions much less frequent.
● At world imply temperatures of two°C above pre-industrial ranges, large-scale chilly spells as uncommon as this one are projected to be about one other 2.5 °C much less chilly for the realm common and about one other 2 °C much less chilly for Oslo. They may turn into even much less frequent than at the moment.
● Local weather change doesn’t imply that chilly waves will now not occur. Actually, much less extreme and fewer frequent chilly waves could also be extra impactful than previous ones if threat notion and preparedness lower because of the much less frequent occasion occurrences.








