A Spanish analysis group has investigated how thermoelectric warmth pumps could also be used as power-to-heat know-how to extend temperatures in thermal power storage techniques. It discovered the proposed system configuration might obtain an general effectivity of 112.6% at at 135 C.
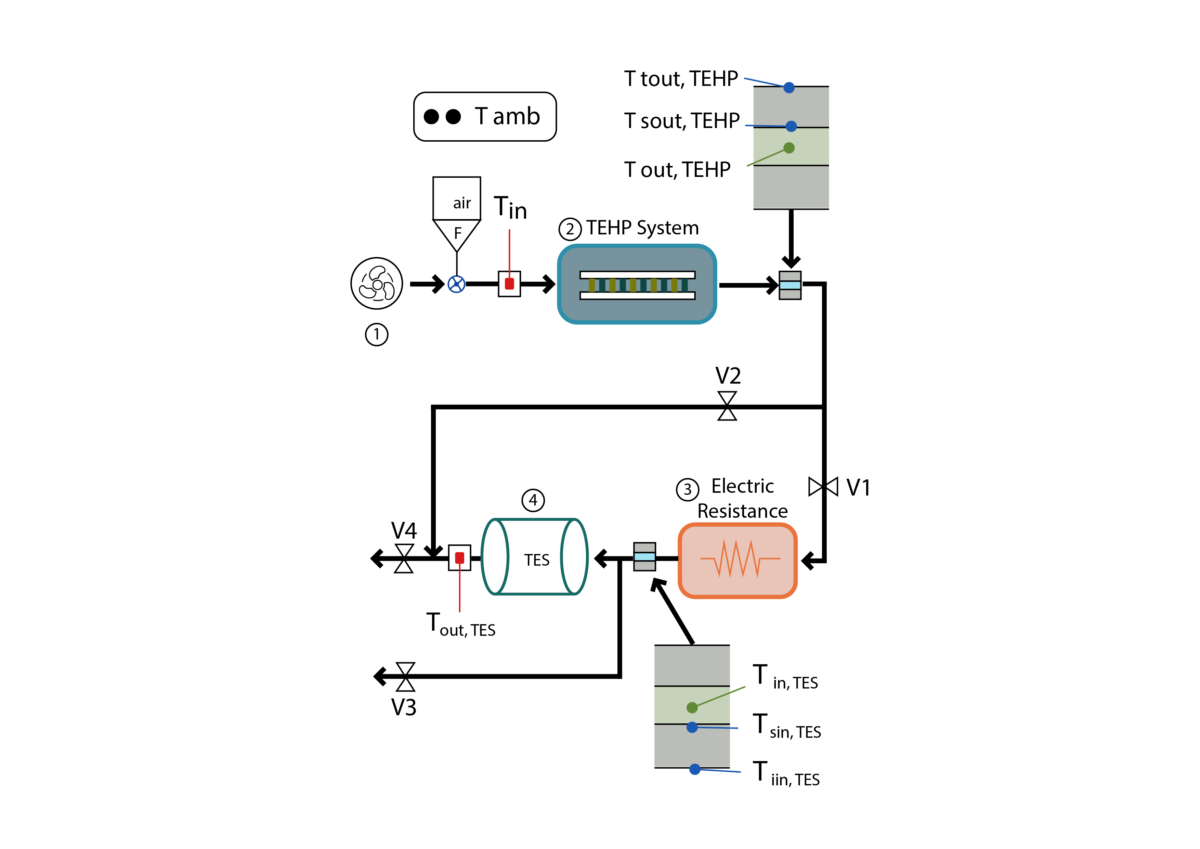
Researchers from Spain have designed a novel thermal power storage (TES) system that makes use of a thermoelectric warmth pump (TEHP) as a power-to-heat know-how to achieve elevated temperatures in charging the storage system itself.
“The evaluation focuses on assessing the coefficient of efficiency (COP) and heating capability by various the voltage provide and the airflow price,” the scientists defined, noting that the TEHP is used as a substitute for variable conductance warmth pipes (VCHPs).
The novel design consists of 4 foremost elements, particularly a thermoelectric warmth pump system, an electrical resistance, and a TES cycle that depends on an open cycle with air as a warmth switch fluid. The fan is positioned on the cycle’s air inlet, and the pushed air is then heated by the TEHP, which makes use of thermoelectric modules (TEMs) with complementing electrical resistance.
“TEMs are generally fashioned by two ceramic plates and a number of other thermocouples fashioned by n- and p-semiconductor junctions, linked thermally in parallel and electrically in collection,” the lecturers stated. “When a present is equipped, warmth is pumped from the chilly sink to the new sink by the Peltier impact.”
The thermoelectric a part of the system is constructed of six TEHP blocks. The primary three use a one-stage thermoelectric warmth pump (OTEHP) configuration, every utilizing a TEM with one warmth exchanger on all sides. The next three TEHP blocks comprise two-stage thermoelectric warmth pumps (TTEHP) with a pyramidal configuration.
“The design of this intermediate warmth exchanger makes use of a extremely environment friendly system comprised of 4 warmth pipe tubes with water as working fluid,” added the researchers. “The switch of warmth from the primary stage to the second stage happens by means of these tubes by way of section change of water.”
Standard content material
The researchers additionally constructed a system prototype and examined 45 situations with completely different voltages within the resistor, storage inlet temperature, and airflow charges. The voltages have been 4 V, 6 V, 8 V, or 10 V; the inlet temperatures have been 120 C, 160 C, or 200 C; and the airflow charges have been 13 m3/hour, 18 m3/hour, or 23 m3/hour.
“With the very best studied airflow price (23 m3/h), 655.5 W of warmth may be generated with a COP of 1.35, elevating the airflow temperature from the ambient temperature to 113.1 C,” the group concluded. “The combination of the developed TEHP system into the charging technique of a thermal power storage system based mostly on electrical resistances will increase the power conversion effectivity by 15% and 30% for power storage temperatures between 120 C and 200 C.”
The teachers additionally discovered the proposed system configuration might obtain an general effectivity of 112.6% at 135 C.
The system was offered within the paper “Enhancement of the Power-to-Heat Energy Conversion Process of a Thermal Energy Storage Cycle through the use of a Thermoelectric Heat Pump,” printed in Utilized Thermal Engineering. The analysis crew was fashioned by scientists from the Public College of Navarre, the National Renewable Energy Centre of Spain, and the Industry Association of Navarra.
Trying ahead, they stated they wish to perceive the system’s conduct beneath various chilly supply temperatures and discover the usage of completely different heating fluids, together with the mixing of phase change materials (PCMs).
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and wish to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.