A merciless consequence of superior most cancers is the profound apathy many sufferers expertise as they lose curiosity in once-cherished actions. This symptom is a part of a syndrome known as cachexia, which impacts about 80% of late-stage most cancers sufferers, resulting in extreme muscle losing and weight reduction that depart sufferers bone skinny regardless of sufficient diet.
This lack of motivation doesn’t simply deepen sufferers’ struggling, it isolates them from household and buddies. As a result of sufferers battle to interact with demanding therapies that require effort and persistence, it additionally strains households and complicates remedy.
Medical doctors sometimes assume that when late-stage most cancers sufferers withdraw from life, it’s an inevitable psychological response to bodily deterioration. However what if apathy isn’t only a byproduct of bodily decline however an integral a part of the illness itself?
In our newly printed analysis, my colleagues and I’ve found one thing exceptional: Most cancers doesn’t merely waste the physique – it hijacks a selected mind circuit that controls motivation. Our findings, printed within the journal Science, problem many years of assumptions and recommend it is perhaps attainable to revive what many most cancers sufferers describe as most devastating to lose – their will to interact with life.

ArtistGNDphotography/E+ through Getty Pictures
Untangling fatigue from bodily decline
To unravel the puzzle of apathy in most cancers cachexia, we would have liked to hint the precise path irritation takes within the physique and peer inside a residing mind whereas the illness is progressing – one thing unattainable in individuals. Nonetheless, neuroscientists have superior applied sciences that make this attainable in mice.
Trendy neuroscience equips us with a robust arsenal of instruments to probe how illness adjustments mind exercise in mice. Scientists can map total brains on the mobile degree, observe neural exercise throughout habits, and exactly change neurons on or off. We used these neuroscience instruments in a mouse mannequin of most cancers cachexia to review the consequences of the illness on the mind and motivation.
We recognized a small mind area known as the world postrema that acts because the mind’s irritation detector. As a tumor grows, it releases cytokines − molecules that set off irritation − into the bloodstream. The world postrema lacks the everyday blood-brain barrier that retains out toxins, pathogens and different molecules from the physique, permitting it to instantly pattern circulating inflammatory indicators.
When the world postrema detects an increase in inflammatory molecules, it triggers a neural cascade throughout a number of mind areas, in the end suppressing dopamine launch within the mind’s motivation heart − the nucleus accumbens. Whereas generally misconstrued as a “pleasure chemical,” dopamine is definitely related to drive, or the willingness to place in effort to achieve rewards: It suggestions the interior cost-benefit scale towards motion.
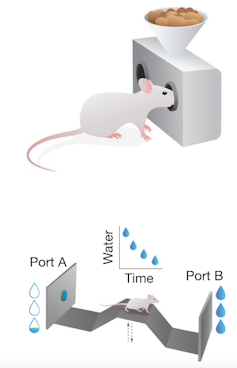
Reprinted with permission from XA Zu et al., Science 388:eadm8857 (2025)
We instantly noticed this shift utilizing two quantitative assessments designed with behavioral economics rules to measure effort. Within the first, mice repeatedly poked their noses right into a meals port, with progressively extra pokes required to earn every meals pellet. Within the second process, mice repeatedly crossed a bridge between two water ports, every steadily depleting with use and forcing the mice to change sides to replenish the provision, much like selecting berries till a bush is empty.
As most cancers progressed, mice nonetheless pursued simple rewards however rapidly deserted duties requiring better effort. In the meantime, we watched dopamine ranges fall in actual time, exactly mirroring the mice’s lowering willingness to work for rewards.
Our findings recommend that most cancers isn’t simply typically “carrying out” the mind − it sends focused inflammatory indicators that the mind detects. The mind then responds by quickly lowering dopamine ranges to dial down motivation. This matches what sufferers describe: “All the pieces feels too laborious.”
Restoring motivation in late-stage illness
Maybe most enjoyable, we discovered a number of methods to revive motivation in mice affected by most cancers cachexia − even when the most cancers itself continued progressing.
First, by genetically switching off the inflammation-sensing neurons within the space postrema, or by instantly stimulating neurons to launch dopamine, we have been capable of restore regular motivation in mice.
Second, we discovered that giving mice a drug that blocks a specific cytokine − working equally to present FDA-approved arthritis therapies − additionally proved efficient. Whereas the drug didn’t reverse bodily losing, it restored the mice’s willingness to work for rewards.
Whereas these outcomes are primarily based on mouse fashions, they recommend a remedy risk for individuals: Focusing on this particular inflammation-dopamine circuit might enhance high quality of life for most cancers sufferers, even when the illness stays incurable.
The boundary between bodily and psychological signs is an artificially drawn line. Most cancers ignores this division, utilizing irritation to commandeer the very circuits that drive a affected person’s will to behave. However our findings recommend these messages may be intercepted and the circuits restored.

FG Commerce/E+ through Getty Pictures
Rethinking apathy in illness
Our discovery has implications far past most cancers. The inflammatory molecule driving lack of motivation in most cancers can also be concerned in quite a few different situations − from autoimmune issues equivalent to rheumatoid arthritis to power infections and melancholy. This identical mind circuit may clarify the debilitating apathy that tens of millions of individuals affected by varied power illnesses expertise.
Apathy triggered by irritation might have initially developed as a protecting mechanism. When early people confronted acute infections, dialing down motivation made sense − it conserved vitality and directed sources towards restoration. However what as soon as helped individuals survive short-term diseases turns dangerous when irritation persists chronically, because it does in most cancers and different illnesses. Relatively than aiding survival, extended apathy deepens struggling, worsening well being outcomes and high quality of life.
Whereas translating these findings into therapies for individuals requires extra analysis, our discovery reveals a promising goal for remedy. By intercepting inflammatory indicators or modulating mind circuits, researchers might be able to restore a affected person’s drive. For sufferers and households watching motivation slip away, that risk presents one thing highly effective: hope that whilst illness progresses, the essence of who we’re is perhaps reclaimed.


